|
Notice: This page contains information for the legacy Phidget21 Library. Phidget21 is out of support. Bugfixes may be considered on a case by case basis. Phidget21 does not support VINT Phidgets, or new USB Phidgets released after 2020. We maintain a selection of legacy devices for sale that are supported in Phidget21. We recommend that new projects be developed against the Phidget22 Library.
|
Template:RTDinfo
Measuring Resistive Thermal Devices (RTD)
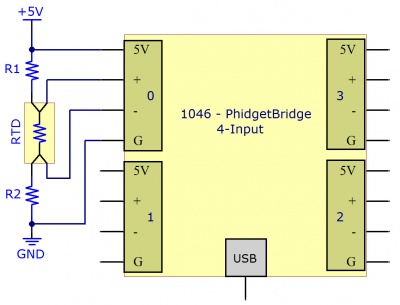
Using a Wheatstone Bridge
A Wheatstone bridge is the classic method of measuring unknown resistances, and requires three resistors of known values. It uses the current in each leg of the bridge to create a voltage differential between both voltage dividers. Using the voltage differential and the three known resistors, the resistance of the fourth resistor can be determined.
To determine the resistance of the RTD, the following formula can be used:
Where is the Bridge Value given by the PhidgetBridge (in mV/V) , and , and are the resistances of the known resistors.
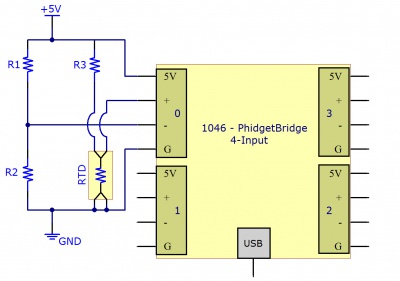
Using a Voltage Divider
The alternate method requires only two resistors. This reduces the amount of error that can be introduced into the system due to resistor tolerances. A voltage is applied to the two resistors and the RTD in series. The voltage drop across the RTD is measured. Using the voltage drop and the values of the two resistors, the resistance of the RTD can be determined.
To determine the resistance of the RTD, the following formula can be used:
Where is the Bridge Value given by the PhidgetBridge (in mV/V) , and and are the resistances of the known resistors.
Getting Higher Accuracy
In order to get the highest accuracy from the RTD, consider the following:
- Use resistors with a high degree of tolerance. There will be less variability in the manufacturing of 0.1% resistors when compared to 1% resistors.
- Measure the known resistors with an ohmmeter. By obtaining the most accurate measurements for the known resistances, the formula will result in a more accurate measurement of the RTD.
- Use a moving average when obtaining the Bridge Value to reduce the amount of noise in the measured signal.
- Estimate or Measure the resistance of the +5V and GND wires between the RTD and the 1046 PhidgetBridge. Add this resistance to the two resistors.
- Turn off the power to the RTD (by disabling the channel on the PhidgetBridge) to reduce self-heating of the RTD.
- By using higher resistor values (> 1 Kilo ohm), there will be less self-heating of the RTD, but the resolution of the measurement will be reduced somewhat. We recommend 1 Kilo Ohm resistors as a reasonable trade off.

![R_{RTD} = \frac{R_3 \times [R_2 + V_B \times (R_1 + R_2)]}{R_1 - (R_1 + R_2) \times V_B }](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/f9b5eaa5340732e841a084db3919b85e2ae44eb0)